概述
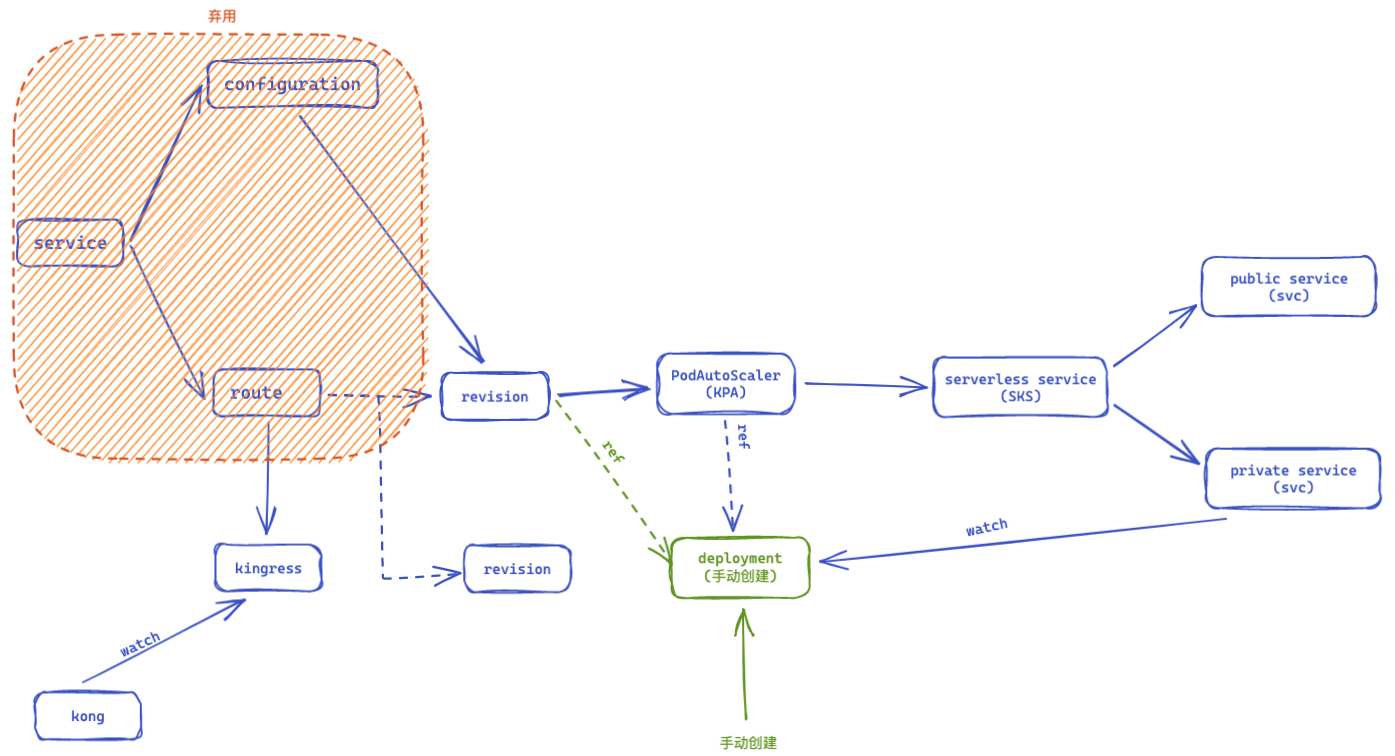
经过前面的介绍,可以发现revision资源是整个流程的核心。那么在不对当前deployment部署托管的情况下。修改revision引用指定的deployment,那么在接受可以对deployment进行有限修改的情况下。就可以直接创建一个revision,让deployment自动获得对应的自动扩缩容的能力。从事后来看,通过这种方式,只需要对deployment增加一个revision name的label以及注入代理pod的修改就够了。通过这种修改方式,ksvc、configuration、route资源就可以弃用了。
本文以以上案例修改的形式,促进对knative各个组件的了解。在目前的流程中deployment是由revision创建的。如果deployment是手动创建的,并且已经为deployment注入了queue容器和添加了revision的label。修改revision将其改为引用deployment。接下来看看我们需要为之适配修改哪些内容。
如何开发
在hack文件夹下是一些列辅助开发的脚本。对于接下来的例子,会用到其中update-codegen.sh 这个脚本来更新自动生成的k8s client代码文件。对于k8s 自定义controller开发来说,这是一个非常常见的行为。
CRD修改增加引用
由于此次的修改目标是revision,所以首先找到revision crd 定义的地方,pkg/apis/serving/v1/revision_types.go由于引用的ref结构在podautoscaler中有,所以我们直接拷贝过来就可以,
Revisioin spec 如下所示,增加了ScaleTargetRef的引用。
// RevisionSpec holds the desired state of the Revision (from the client).
type RevisionSpec struct {
corev1.PodSpec `json:",inline"`
// ContainerConcurrency specifies the maximum allowed in-flight (concurrent)
// requests per container of the Revision. Defaults to `0` which means
// concurrency to the application is not limited, and the system decides the
// target concurrency for the autoscaler.
// +optional
ContainerConcurrency *int64 `json:"containerConcurrency,omitempty"`
// ScaleTargetRef defines the /scale-able resource that this Revision
// is responsible for quickly right-sizing. If containers is an empty array
// and ScaleTargetRef is defined, will not create a container.
ScaleTargetRef *corev1.ObjectReference `json:"scaleTargetRef,omitempty"`
// TimeoutSeconds is the maximum duration in seconds that the request routing
// layer will wait for a request delivered to a container to begin replying
// (send network traffic). If unspecified, a system default will be provided.
// +optional
TimeoutSeconds *int64 `json:"timeoutSeconds,omitempty"`
}
改完之后,在执行完./hack/update-codegen.sh之后,你会发现在创建带有scaleTargetRef的revision的时候在创建时被拒绝了,这是因为前面说到的webhook校验逻辑造成的。那么针对这个修改还需要在pkg/apis/serving/v1/revision_validation.go文件中修改校验逻辑,如果定义了scaleTargetRef那么就校验scaleTargetRef定义合法性,而不对PodSpec部分进行校验允许不定义此部分内容。
// Validate implements apis.Validatable
func (rs *RevisionSpec) Validate(ctx context.Context) *apis.FieldError {
var errs *apis.FieldError
// If ScaleTargetRef appears, pod spec will not be used
if rs.ScaleTargetRef != nil {
errs = serving.ValidateNamespacedObjectReference(rs.ScaleTargetRef).
ViaField("scaleTargetRef")
} else {
errs = serving.ValidatePodSpec(ctx, rs.PodSpec)
}
// ......
}
在修改完之后就可以创建带有引用的crd了。但是这个crd并不能按预期行为进行,因为我们将pod定义改成了deployment的ref引用。接下来要修改的就是controller的行为,使其在引用dp的模式下不再创建deployment。
引用模式下不创建deployment
前面说到过对于这个crd的修改会在pkg/reconciler/revision中,首先查找到ReconcileKind函数在pkg/reconciler/revision/revision.go文件中,通过对这个函数的查看找到创建deployment的逻辑函数是在pkg/reconciler/revision/reconcile_resources.go文件中的reconcileDeployment函数,只需要修改在存在ref的时候不再创建dp就可以。
另外还需要找到创建PodAutoscaler部分,修改引用注入的方式,去掉其他无关代码,就是如果revision设置了引用那么就将PodAutoscaler的引用设置为引用。
func MakePA(rev *v1.Revision) *autoscalingv1alpha1.PodAutoscaler {
deploymentName := names.Deployment(rev)
if rev.Spec.ScaleTargetRef != nil {
deploymentName = rev.Spec.ScaleTargetRef.Name
}
return &autoscalingv1alpha1.PodAutoscaler{
Spec: autoscalingv1alpha1.PodAutoscalerSpec{
ScaleTargetRef: corev1.ObjectReference{
APIVersion: "apps/v1",
Kind: "Deployment",
Name: deploymentName,
},
},
}
}
小脑洞
固定的配置通常难以估计出一个服务正常的流量限制,而自适应限流通常都是计算服务的一个理想时延带宽比。假设以BBR为例,计算服务在满负载下的请求带宽时延,反向估算出服务的最大通行TPS,然后以这个TPS为阈值进行扩容计算。感觉可能有机会自适应扩容。
knative跟service mesh的结合目前还是各成体系,只是能工作在一起,但是不能相互成就。最起码自适应限流的信号是可以流入knative控制信号的。
这部分代码修改可以在feat_route_ref分支上看到。此分支基于knative 0.26版本修改。